Two weeks ago, Italy had 322 confirmed cases of the coronavirus. At that point, doctors in the country’s hospitals could lavish significant attention on each stricken patient.
One week ago, Italy had 2,502 cases of the virus, which causes the disease known as COVID-19. At that point, doctors in the country’s hospitals could still perform the most lifesaving functions by artificially ventilating patients who experienced acute breathing difficulties.
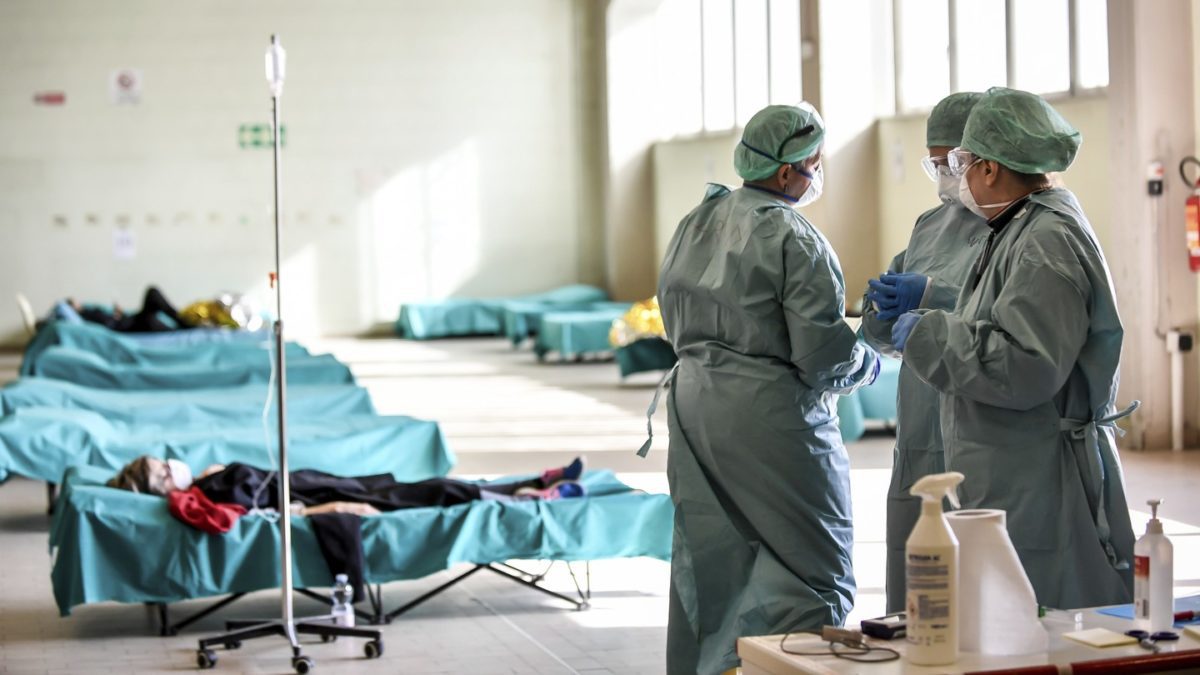
Today, Italy has 10,149 cases of the coronavirus. There are now simply too many patients for each one of them to receive adequate care. Doctors and nurses are unable to tend to everybody. They lack machines to ventilate all those gasping for air.
Now the Italian College of Anesthesia, Analgesia, Resuscitation and Intensive Care (SIAARTI) has published guidelines for the criteria that doctors and nurses should follow as these already extraordinary circumstances worsen. The document begins by likening the moral choices Italian doctors may face to the forms of wartime triage that are required in the field of “catastrophe medicine.” Instead of providing intensive care to all patients who need it, the authors suggest, it may become necessary to follow “the most widely shared criteria regarding distributive justice and the appropriate allocation of limited health resources.”
The principle they settle upon is utilitarian. “Informed by the principle of maximizing benefits for the largest number,” they suggest that “the allocation criteria need to guarantee that those patients with the highest chance of therapeutic success will retain access to intensive care.”